Params and Query Params
How to use Params and Query Params
Tupã provides the necessary functions to obtain both request parameters and query parameters.
To do this, you can use the functions Param(param), QueryParam(), QueryParams().
Obtaining the request parameter To easily obtain the request parameter, put the parameter name in the URL using the syntax /{param}, then call the Param(param) function available from the TupaContex
func main() { server := tupa.NewAPIServer(":6969", exampleManager) server.RegisterRoutes(tupa.GetRoutes()) server.New()}
func SampleRouteManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/{jwt}", Method: "GET", Handler: func(tc *tupa.TupaContext) error { param := tc.Param("jwt") tc.SendString(fmt.Sprintf("jwt:, %s", param))
return nil }, }, }}Now at http://localhost:6969/

Obtaining Query Param from the request
Similarly, we can obtain a single Query Param using the QueryParam() method. This method will return a specific parameter from our URL, so if we specify multiple parameters, it will only return the specified one.
Let’s define a route called /param and make the call using a Query Parameter, so the end of the URL will be /param?<param_name>=<param_value>.
func main() { server := tupa.NewAPIServer(":6969", exampleManager) server.RegisterRoutes(tupa.GetRoutes()) server.New()}
func exampleManager() { tupa.AddRoutes(nil, SampleRouteManager)}
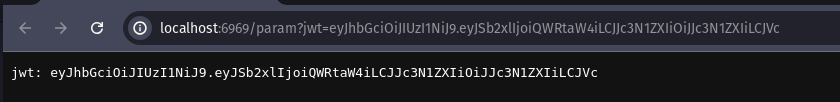
func SampleRouteManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/param", Method: "GET", Handler: func(tc *tupa.TupaContext) error { param := tc.QueryParam("jwt") tc.SendString(fmt.Sprintf("jwt: %s", param))
return nil }, }, }}Let’s make a GET request to the URL http://localhost:6969/param?jwt=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJSb2xlIjoiQWRtaW4iLCJJc3N1ZXIiOiJJc3N1ZXIiLCJVc.
Output:
NOTE: As mentioned earlier, if more than one parameter is passed, this method will only get the one specified in the argument. We can check this functionality.
Let’s pass 2 arguments in the URL and make a request to http://localhost:6969/param?jwt=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJSb2xl&name=victor.
func main() { server := tupa.NewAPIServer(":6969", exampleManager) server.RegisterRoutes(tupa.GetRoutes()) server.New()}
func exampleManager() { tupa.AddRoutes(nil, SampleRouteManager)}
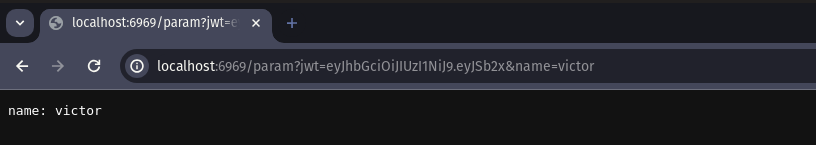
func SampleRouteManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/param", Method: "GET", Handler: func(tc *tupa.TupaContext) error { param := tc.QueryParam("name") tc.SendString(fmt.Sprintf("name: %s", param))
return nil }, }, }}Output:
Obtaining Multiple Query Params from the request
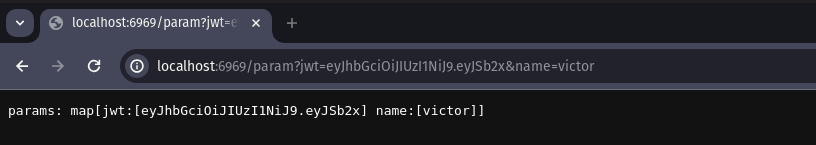
We can easily obtain multiple Query Params from our request using the QueryParams() method, which will return a map[string][]string, that is, parameter: [values].
func main() { server := tupa.NewAPIServer(":6969", exampleManager) server.RegisterRoutes(tupa.GetRoutes()) server.New()}
func exampleManager() { tupa.AddRoutes(nil, SampleRouteManager)}
func SampleRouteManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/param", Method: "GET", Handler: func(tc *tupa.TupaContext) error { param := tc.QueryParams() tc.SendString(fmt.Sprintf("params: %s", param))
return nil }, }, }}Let’s make the same call to http://localhost:6969/param?jwt=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJSb2xl&name=victor.
Output: