Middlewares
How to create Middlewares
Using middlewares in Tupã is easy. We can implement middlewares both at the route level, sets of routes and global middlewares.
Let’s add a simple middleware at the route level. Just add a new Middlewares property inside the endpoint object.
Let’s add a middleware to the /cats route.
func main() { routeManagerExample := func() { routes := func() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/", Method: "GET", Handler: func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { return tupa.WriteJSONHelper(c.Resp, http.StatusOK, "Hello world! :D") }, }, { Path: "/cats", Method: "GET", Handler: func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { resp, err := http.Get("https://cdn2.thecatapi.com/images/dN6eoeLjY.jpg") if err != nil { return err } defer resp.Body.Close() _, err = io.Copy(c.Resp, resp.Body) return err }, Middlewares: []tupa.MiddlewareFunc{ MiddlewareSampleCats, }, }, } }
tupa.AddRoutes(nil, routes) }
server := tupa.NewAPIServer(":6969", routeManagerExample)
server.RegisterRoutes(routeInfo) server.New()}
func MiddlewareSampleCats(next tupa.APIFunc) tupa.APIFunc { return func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { c.Resp.Header().Set("Content-Type", "image/jpeg") c.Resp.Header().Add("Referrer-Policy", "someone interested in cats") return next(c) }}We can obtain the result of the above middleware, just press F12 and check the request in the Network tab of our devtools.
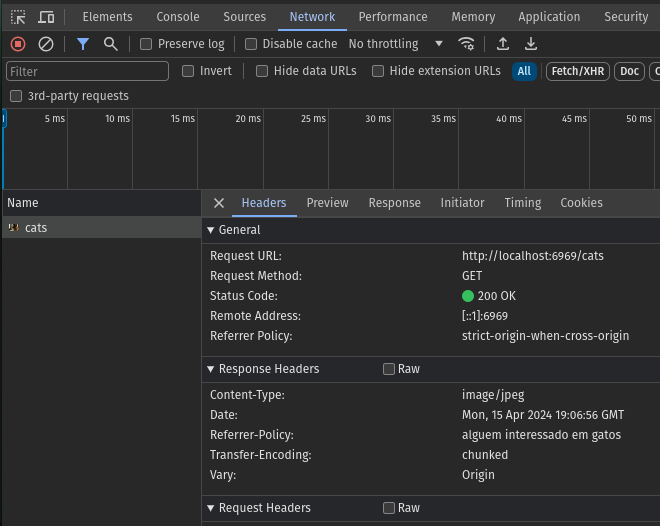
Different Middlewares for Sets of Routes
But it may be that we want to add different middlewares for different sets of routes. In this case, we can store our routes in functions and call the GetRoutes() method from Tupã as a parameter to the RegisterRoutes() function. See an example below:
func main() { server := tupa.NewAPIServer(":6969", exampleManager()) server.New()}
func MiddlewareSampleCats(next tupa.APIFunc) tupa.APIFunc { return func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { c.Resp.Header().Set("Content-Type", "image/jpeg") c.Resp.Header().Add("Referrer-Policy", "someone interested in cats") return next(c) }}
func exampleManager() { tupa.AddRoutes(nil, SampleViewsManager) tupa.AddRoutes(tupa.MiddlewareChain{MiddlewareSampleCats}, SampleRouteManager)}
func SampleViewsManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/", Method: "GET", Handler: func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { return tupa.WriteJSONHelper(c.Resp, http.StatusOK, "Hello world! :D") }, }, }}
func SampleRouteManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/cats", Method: "GET", Handler: func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { resp, err := http.Get("https://cdn2.thecatapi.com/images/dN6eoeLjY.jpg") if err != nil { return err } defer resp.Body.Close() _, err = io.Copy(c.Resp, resp.Body) return err }, }, }}Middlewares in Sets of Routes + Specific Routes
We can also add middlewares for sets of routes and specific routes together. In this case, the order will be that the specific route middlewares will take precedence over the group ones in execution. Let’s see in the following code:
func main() { server := tupa.NewAPIServer(":6969", exampleManager()) server.New()}
func MiddlewareSampleCats(next tupa.APIFunc) tupa.APIFunc { return func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { fmt.Println("Printed after") return next(c) }}
func MiddlewareSampleRoute(next tupa.APIFunc) tupa.APIFunc { return func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { fmt.Println("Printed before") c.Resp.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/plain") c.Resp.Header().Add("Referrer-Policy", "someone interested in cats") return next(c) }}
func exampleManager() { tupa.AddRoutes(nil, SampleViewsManager) tupa.AddRoutes(tupa.MiddlewareChain{MiddlewareSampleCats}, SampleRouteManager)}
func SampleViewsManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/", Method: "GET", Handler: func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { return tupa.WriteJSONHelper(c.Resp, http.StatusOK, "Hello world! :D") }, }, }}
func SampleRouteManager() []tupa.RouteInfo { return []tupa.RouteInfo{ { Path: "/cats", Method: "GET", Handler: func(c *tupa.TupaContext) error { resp, err := http.Get("https://cdn2.thecatapi.com/images/dN6eoeLjY.jpg") if err != nil { return err } defer resp.Body.Close() _, err = io.Copy(c.Resp, resp.Body) return err }, Middlewares: []tupa.MiddlewareFunc{MiddlewareSampleRoute}, }, }}Output:
Server started on port: :6969Printed beforePrinted afterHowever, in some cases, we will need to store some data after any request is completed and after all sets of AfterMiddlewares. For this, we should use the Global Middlewares.
